Sometimes a computer chess engine will recommend a line of play which is "objectively" better than an alternative that a human might choose. Yet there might be good reasons to choose the "worse" line of play, if it is tricky and has some traps. See the note to Black's 7th move.
On the other hand, sometimes "human" moves fall short, as well. See the note to Black's 9th move.
Wall, Bill - Guest902091
PlayChess.com, 2017
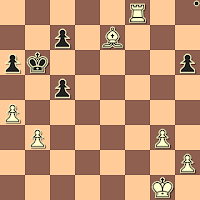
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.d4 Nf6
Black has so many ways to return some of the sacrificed material!
7.dxe5 Bxf2+
This move appears in 10 previous games appearing in The Database, with White scoring 70%. However, that is not the whole story.
Stockfish 8 recommends, instead 7...Qe7!?, which does not show up in any of the games in The Database. White does best to grab a second piece with 8.exf6, but then is faced with how to answer 8...Qxe4+.
Probably best is 9.Kf1 which we will come back to in a moment, after first examining the messy 9.Be3.
Black can respond to this latter move with 9...Bxe3 10.fxe3 Qxe3+ 11.Qe2 when the exchange of Queens would leave him a pawn up. Or he could go for 11...Qc1+ when 12.Kf2 is the offer of a Rook, i.e. 12...Qxh1, although it does not turn out well for the second player: 13.Qe7+ Kg6 14.Qxg7+ Kf5 15.Nc3 Qxh2 (taking the other Rook with 15...Qxa1 leads to mate) 16.Rf1 and Black's position is miserable as he has only 16...Qf4+ to help him extend the game, but 17.Kg1 Qxf1+ 18.Kxf1 still is hopeless. After visiting c1, Black's Queen should return to f4 with check, and eventually wind up a pawn ahead, again.
Going back to the computer-recommended 9.Kf1, Black responds with 9...Qf5 and after 10.Qf3 Qxf3 11.gxf3 d5!? he is a bit better (better pawn structure, two Bishops, equally insecure Kings) even if White finds 12.h4!? to prevent ...Bh3+, forcing his King into the center where the enemy Rooks can roam.
By the way, Bill dispatched 7...Nxe4 quickly in a couple of games: Wall,B - NN, lichess.org, 2016 (1-0, 16) and Wall,B - TenAndOnly10, lichess.org, 2016 (1-0, 21)
8.Kxf2 Nxe4+ 9.Kg1 Rf8
Preparing to castle-by-hand, a standard defensive plan in the Jerome Gambit; but overlooking the Queen check at d5 - odd, in that his Bishop sacrifice seemed aimed against that same eventuality.
Instead, 9...d5 would be about even, although Bill has a couple of wins against the move: Wall,B - MyDrunkAccount, lichess.org, 2016 (1-0, 20) and Wall,B - Szachowski, playok.com, 2017 (1-0, 20).
10.Qd5+ Ke8 11.Qxe4 Rf7 12.Nc3 d6
This hurries Black's demise.
13.exd6+ Kf8 14.Qxh7 Qxd6 15.Qh8+ Ke7 16.Bg5+ Kd7 17.Rd1 Black resigned
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+ ...and related lines
(risky/nonrisky lines, tactics & psychology for fast, exciting play)
Saturday, January 13, 2018
Thursday, January 11, 2018
Jerome Gambit: Paths Off of Paths
The Jerome Gambit is an opening that is clearly "off the beaten path". Yet, in pursuing it, players often find themselves further afield - and it is good to know about some of those side paths as well.
It is clear in the following game that the defender was not prepared to have the game "Jerome-ized".
Wall, Bill - Guest761989
PlayChess.com, 2017
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Na5 4.Bxf7+
With his third move Black imagines a quiet win of the "minor exchange" with 4.Bb3 Nxb3. He is too hopeful, as White has, instead, 4.Nxe5, and after 4...Nxc4 5.Nxc4 d5 6.exd5 Qxd5 7.Ne3 White is a pawn up, and Black has little to show for it.
However, players familiar with the Jerome Gambit will be tempted to play the Bishop sacrifice on move 4, giving Black a very un-quiet game.
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Ke6 6.d4 d6
White has two pawns for his sacrificed piece, but his play against Black's King gives him adequate compensation.
7.Qg4+ Ke7 8.Qg5+ Ke8
Better is 8...Nf6, although after 9.Nf3 Nc6 10.e5 dxe5 11.dxe5 Kf7 12.exf6 Qxf6 White would have a small advantage.
9.Qxd8+
It is important to note that in the 4 earlier games in The Database, White had tried 9.Qh5+. Best play would continue 9...g6 10.Nxg6 Nf6 11.Qh4 hxg6 12.Qxh8 Nxe4 When White would have a Rook and two pawns against a Bishop and a Knight. This is a small edge for White, and I can see why Bill chose a different path: His active Knights will go after the slumbering Rooks in the corners!
9...Kxd8 10.Nf7+ Ke8 11.Nxh8 g6 12.Nc3 Bg7
As indicated.
13.Nd5 c6 14.Nc7+ Black resigned
Black will lose his other Rook, and while he will gather in the Knight at h8, he will have a very difficult time catching the other one, leaving him down a couple of exchanges, plus a pawn or two.
It is clear in the following game that the defender was not prepared to have the game "Jerome-ized".
Wall, Bill - Guest761989
PlayChess.com, 2017
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Na5 4.Bxf7+
With his third move Black imagines a quiet win of the "minor exchange" with 4.Bb3 Nxb3. He is too hopeful, as White has, instead, 4.Nxe5, and after 4...Nxc4 5.Nxc4 d5 6.exd5 Qxd5 7.Ne3 White is a pawn up, and Black has little to show for it.
However, players familiar with the Jerome Gambit will be tempted to play the Bishop sacrifice on move 4, giving Black a very un-quiet game.
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Ke6 6.d4 d6
White has two pawns for his sacrificed piece, but his play against Black's King gives him adequate compensation.
7.Qg4+ Ke7 8.Qg5+ Ke8
Better is 8...Nf6, although after 9.Nf3 Nc6 10.e5 dxe5 11.dxe5 Kf7 12.exf6 Qxf6 White would have a small advantage.
9.Qxd8+
It is important to note that in the 4 earlier games in The Database, White had tried 9.Qh5+. Best play would continue 9...g6 10.Nxg6 Nf6 11.Qh4 hxg6 12.Qxh8 Nxe4 When White would have a Rook and two pawns against a Bishop and a Knight. This is a small edge for White, and I can see why Bill chose a different path: His active Knights will go after the slumbering Rooks in the corners!
9...Kxd8 10.Nf7+ Ke8 11.Nxh8 g6 12.Nc3 Bg7
As indicated.
13.Nd5 c6 14.Nc7+ Black resigned
Black will lose his other Rook, and while he will gather in the Knight at h8, he will have a very difficult time catching the other one, leaving him down a couple of exchanges, plus a pawn or two.
Tuesday, January 9, 2018
The Delayed Pie-in-the-Face
The difference between a very strong counter in the Jerome Gambit at move 6 and an ineffective defensive line (the same move one tempo later) shows the problem with delaying an active riposte.
Wall, Bill - Guest6766281
PlayChess.com, 2017
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.d4 Bb6
Black can decide which piece to save, the Bishop or the Knight. The text is a reasonable line.
Of course, Black's strongest response is to ignore both of the pieces and play 6...Qh4!?, what I have referred to as a pie-in-the-face variation.
7.dxe5 Qh4
A delayed pie-in-the-face? Tossing pies is very much a part of slapstick humor - and timing is always critical in comedy.
This line has been faced by Jerome Gambiteers chessmanjeff, frizerkaHR, GOH, HauntedKnight, jfhumphrey, ndrwgn, stretto, Wall and yorgos. As a group, they have not been impressed.
8.Qf3+ Ke7
A slightly better retreat is 8...Ke8, e.g. 9.Nc3 (9.O-O Ne7 10.Nc3 Rf8 11.Qe2 g5 12.Be3 Ng6 13.Nd5 Kd8 14.Qd2 h6 15.Bxb6 axb6 16.Nxc7 Kxc7 17.Qd6+ Kd8 18.Qxg6 Re8 19.Qxb6+ Ke7 20.Qf6 checkmate, Wall,B - Guest2616286, PlayChess.com, 2017) 9...Ne7 (9...Bxf2+ 10.Qxf2 Qxf2+ 11.Kxf2 Nh6 12.Nd5 Ng4+ 13.Kg3 Kd8 14.Bg5+ Nf6 15.exf6 h6 16.fxg7+ Ke8 17.gxh8=Q+ Kf7 18.Rhf1+ Kg6 19.Qxh6 checkmate, Wall,B - Shillam, lichess.org, 2016) 10.g3 Qh3 11.Be3 d6 12.Bxb6 cxb6 13.exd6 Ng6 14.Nd5 Qd7 15.Nc7+ Kd8 16.Nxa8 Qxd6 17.Rd1 Ne5 18.Rxd6+ Ke7 19.Qc3 Kxd6 20.Qd4+ Ke6 21.Nc7+ Kf7 22.Qxe5 Rd8 23.Nb5 Bg4 24.Qf4+ Kg8 25.Qxg4 a6 26.Qe6+ Kh8 27.Nd6 Rb8 28.Nf7+ Kg8 29.Nh6+ Kh8 30.Qg8+ Rxg8 31.Nf7 checkmate, Wall,B - Itboss, lichess.org, 2016.
9.Nc3
Or 9.O-O Nh6 10.Nc3 Rf8 11.Nd5+ Kd8 12.Qxf8 checkmate, Wall,B - Guest2293428, PlayChess.com, 2017.
9...Nh6 10.Nd5+ Kd8
Once again, e8 is the better square for the King.
11.O-O
White also has the sneaky 11.h3!? threatening g2-g3, winning the Queen. Black could escape by returning a piece for two pawns, i.e. 11...Bxf2+ 12. Qxf2 Qxe4+ but White would be better.
For the record, 11.g3?! directly could be answered by 11...Qg4 and White does not gain much by exchanging Queens, while he would lose time if he movee his Queen to avoid the swap.
11...Bd4
Looking to grab the pawn at e5, but he is overlooking a few things. He could have maintained an even game with 11...c6 12.Nxb6 axb6.
12.g3 Qh3
Why was e8 the better square for Black's King to retreat to (as suggested in the note to move 10)?
Why was the Black Bishop's trip to d4 problematic (as mentioned in the note to move 11)?
Why couldn't Black retreat his Queen to g4 (as in the note to move 11), instead of h3?
13.Bg5+ Ke8 14.Nxc7 checkmate
Sunday, January 7, 2018
Jerome Gambit: Skeptical Defense
Wall, Bill - Guest673244
PlayChess.com, 2017
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.Qh5+
This is interesting. Bill usually plays 6.d4.
6...Ng6 7.Qd5+ Kf8 8.Qxc5+ d6 9.Qe3 Nf6 10.Nc3 Be6
Black develops a piece, and remains slightly better.
Despite the fact that his King is uncastled - and, therefore, he might feel more comfortable not opening up the position - Black could have played 10...d5, and after 11.exd5 Kf7 12.0-0 Re8 13.Qd4 c6 he would have recovered his sacrificed pawn and his prospects would have been brighter than in the game.
11.b3
Feeling adventurous, Bill bypasses the thematic 11.f4 and the reliable 11.d4 for a chance to put his Bishop on the long diagonal. We have seen this strategy for White before: why hurry? Let Black figure things out on his own.
11...Kf7 12.Bb2 Re8 13.O-O-O Kg8
Black has played steadily, developing his pieces and castling-by-hand.
This is just the kind of position that could feature opposite wing pawn storms, and White wastes no time in getting his started.
14.h4 Ng4
Black is not convinced. He could have tried 14...d5 or 14...h5 instead.
15.Qg3 Nf6 16.h5 Ne5
17.f4 Neg4 18.f5 Bf7 19.h6
This is what Bill is looking for: to open the h-file for his Rook, the g-file for his Queen, and the a1-h8 diagonal for his Bishop.
Black can stop White's plan, but he will have to give back some material.
19...gxh6
Instead, 19...d5 20.Rh4!? Qd6 21.Rxg4 Nxg4 22.Qxg4 Qxh6 23.Nxd5 would have helped on defense, although White would have two pawns for the exchange, and the initiative.
20.Rxh6 Kf8 21.Qf4
21...Re5
Black remains skeptical, and it is easy to see why. Take, for example, his best defense, instead of the text: 21...Nxh6 22.Qxh6+
Ke7 His King appears to be escaping trouble, and he has an extra Rook (for two pawns). However, if White finds 23.Nb5!?, uncovering the Bishop, then after 23...Nh5 24.g4 Kd7 25.Qxh7 Re7 26.gxh5 he will have 3 pawns for the exchange - and the pawns will become more dangerous with each step forward.
22.d4 Re8
Come and get me, says Black.
23.e5
As you wish, says White.
23...Ng8
Tougher was 23...Qe7, when 24.Rxf6 Nxf6 25.Qh6+ Kg8 again leaves White a Rook down, but 26.Rh1 (better than 26.Rd3) Nh5 27.Ne4!? Qf8 28.Rxh5 Qxh6+ 29.Rxh6 again puts the first player in the better position, with two pawns for the exhange - and his pawns are ready to cause trouble.
24.Rxh7 Black resigned
I think Black was worn out and no longer skeptical. His Knight on g4 is hanging, his Bishop is threatened with e5-e6, and his King is not going to be able to escape, i.e. 24...Ke7 25.e6, etc.
Stockfish 8 gives as best 24...N4f6, when 25.exf6 Qxf6 26.Nb5!? would be too much for Black to deal with.
PlayChess.com, 2017
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.Qh5+
This is interesting. Bill usually plays 6.d4.
6...Ng6 7.Qd5+ Kf8 8.Qxc5+ d6 9.Qe3 Nf6 10.Nc3 Be6
Black develops a piece, and remains slightly better.
Despite the fact that his King is uncastled - and, therefore, he might feel more comfortable not opening up the position - Black could have played 10...d5, and after 11.exd5 Kf7 12.0-0 Re8 13.Qd4 c6 he would have recovered his sacrificed pawn and his prospects would have been brighter than in the game.
11.b3
Feeling adventurous, Bill bypasses the thematic 11.f4 and the reliable 11.d4 for a chance to put his Bishop on the long diagonal. We have seen this strategy for White before: why hurry? Let Black figure things out on his own.
11...Kf7 12.Bb2 Re8 13.O-O-O Kg8
Black has played steadily, developing his pieces and castling-by-hand.
This is just the kind of position that could feature opposite wing pawn storms, and White wastes no time in getting his started.
14.h4 Ng4
Black is not convinced. He could have tried 14...d5 or 14...h5 instead.
15.Qg3 Nf6 16.h5 Ne5
17.f4 Neg4 18.f5 Bf7 19.h6
This is what Bill is looking for: to open the h-file for his Rook, the g-file for his Queen, and the a1-h8 diagonal for his Bishop.
Black can stop White's plan, but he will have to give back some material.
19...gxh6
Instead, 19...d5 20.Rh4!? Qd6 21.Rxg4 Nxg4 22.Qxg4 Qxh6 23.Nxd5 would have helped on defense, although White would have two pawns for the exchange, and the initiative.
20.Rxh6 Kf8 21.Qf4
21...Re5
Black remains skeptical, and it is easy to see why. Take, for example, his best defense, instead of the text: 21...Nxh6 22.Qxh6+
Ke7 His King appears to be escaping trouble, and he has an extra Rook (for two pawns). However, if White finds 23.Nb5!?, uncovering the Bishop, then after 23...Nh5 24.g4 Kd7 25.Qxh7 Re7 26.gxh5 he will have 3 pawns for the exchange - and the pawns will become more dangerous with each step forward.
22.d4 Re8
Come and get me, says Black.
23.e5
As you wish, says White.
23...Ng8
Tougher was 23...Qe7, when 24.Rxf6 Nxf6 25.Qh6+ Kg8 again leaves White a Rook down, but 26.Rh1 (better than 26.Rd3) Nh5 27.Ne4!? Qf8 28.Rxh5 Qxh6+ 29.Rxh6 again puts the first player in the better position, with two pawns for the exhange - and his pawns are ready to cause trouble.
24.Rxh7 Black resigned
I think Black was worn out and no longer skeptical. His Knight on g4 is hanging, his Bishop is threatened with e5-e6, and his King is not going to be able to escape, i.e. 24...Ke7 25.e6, etc.
Stockfish 8 gives as best 24...N4f6, when 25.exf6 Qxf6 26.Nb5!? would be too much for Black to deal with.
Friday, January 5, 2018
Blackburne Shilling Gambit Investigator: Update
I have written here before about Rodolfo Pardi (see "Blackburne Shilling Gambit Investigator")
Rodolfo was referring to the line 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Nd4 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Ke6 and I thought I would take a closer look at it. The following game holds a lot of analysis and ideas - and also shows the practical side of the Blackburne Shilling Gambit, as complications bring the clock into play.
hanslenz - raidrunner
blitz, FICS, 2012
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Nd4 4.Bxf7+
The Blackburne Shilling Jerome Gambit. The Database has 5,337 game examples. White scores 56%. (Only 2% of the games are draws.)
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Ke6
Black's most enterprising response. Here The Database has 1,434 games, with White scoring 53%.
6.c3 Kxe5 7.cxd4+ Ke6
Wise. Black avoids a whole lot of trouble by declining the d-pawn and the e-pawn. Trust me. Or check out the wild analysis, below.
After 7...Kxd4?! 8.Qb3 we enter a line that shows up in exactly 0 games in The Database, and which has complications galore.
Stockfish 8 recommends 8...d5 (instead, grabbing the second pawn makes matters dangeously worse for Black: 8...Kxe4?! 9.d4! Bb4+!? 10.Nc3+!? Bxc3+ 11.bxc3 Qe7 12.g4!? Qe6 [12...Kf3+ 13.Be3 Kxg4 14.Rg1+ and mates] 13.c4 Qxg4 [13...Kxd4+ 14.Be3+ and mates] 14.Qc2+ Kxd4 15.Qb2+ Kd3 [15...Ke4 16.f3+!? Qxf3 17.Rf1 Qxf1+ 18.Kxf1 and wins] 16.Be3 Ke4 17.h3 Qg6 18.0–0–0 Qf6 19.Bd4 Qf4+ 20.Kb1 Kf5 21.Bxg7 d6 22.Bxh8 Ke6 23.Rhg1 and White is winning) 9.Nc3 Ne7 10.Nb5+!? (Or 10.exd5 Ke5 11.0–0 Kf6 12.d6 Kg6 [12...Nc6 13.Ne4+ Kg6 14.Qg3+ Kf7 15.Ng5+ Kf6 16.b4 Bxd6 17.Bb2+ Be5 18.Bxe5+ Nxe5 19.Ne4+ Kf7 20.Qf4+ Kg6 21.Qxe5] 13.dxe7 Bxe7 14.Re1 Re8 15.d4 Bd6 16.Bd2 h6 17.Nd5 c6 18.Nf4+ Bxf4 19.Bxf4 Rxe1+ 20.Rxe1 Qd5 21.Qxd5 cxd5 22.Re7 Kf6 23.Rc7 g5 1.52/27 ) 10...Ke5 11.Nxc7!? Rb8 (11...Qxc7? 12.Qg3+ Kf6 13.Qxc7) 12.d4+ Kf6 [only move] 13.Bf4 dxe4 14.0–0 h6 15.Rae1 b5 16.Be5+ Kg6 17.Ne6 Bxe6 18.Qxe6+ Kh7 19.Bxb8 Qxb8 20.Rxe4 Qc8 21.g3 Qxe6 22.Rxe6 Nf5 with the advantage to White of R+2P vs N+B.
If Black tries 7...Kxe4?! instead, White has 8.Qf3!? Kxd4 9.Nc3 (there are no games with this move in The Database) and Black will lose material trying to undo the mating web. For example, 9...c6 10.Qe3+ Kc4 11.a4!? Qe7 - trying to keep the White Queen out of the action by pinning it to the King - 12.b3!? and Black will lose his Queen after 12...Kb4 13.Ba3+ or be checkmated after 12...Kxb3 13.Ne4+ Kc4 14.Ba3!? Also a reasonable defensive try is 9...Qe7+, but after the logical 10.Kd1 White's King is far less uncomfortable, for example 10...Nf6 11.Qf4+ Kc5 12.Qxc7+ Kd4 13.Re1, winning the Queen. (See also "Regicide".)
8.O-O
Keeping his options open.
Also seen:
8.Nc3 Kf7 (8...Bb4, instead, is "A casual move that brings much misfortune"; see Clydeco - chaparov, standard, FICS, 2012) 9.Qb3+ (9.Qh5+ g6 10.Qf3+ Qf6 11.Qd3 Bg7 12.e5 Qa6 13.Qf3+ Ke8 14.d3 Ne7 15.O-O Rf8 16.Qh3 h5 17.Qg3 d6 18.Bg5 dxe5 19.Bxe7 Kxe7 20.Nd5+ Kd8 21.dxe5 Bf5 22.e6 Qd6 23.e7+ Ke8 24.exf8=Q+ Bxf8 25.Nxc7+ Kd7 26.Nxa8 Qxg3 27.fxg3 Bc5+ 28.d4 Bxd4+ 29.Kh1 Bxb2 30.Rab1 Bxb1 31.Rxb1 Ba3 32.Rxb7+ Kc6 33.Rxa7 Bc5 34.Rg7 Kb5 35.Rxg6 h4 36.gxh4 Kc4 37.Rg5 Be3 38.Rg3 Bf4 39.Rg4 Kd5 40.Rxf4 Kc6 41.h5 Kd6 42.h6 Ke6 43.h7 Ke5 44.Rf7 Ke6 45.h8=Q Kxf7 46.g4 Ke6 47.g5 Kf7 White ran out of time, Black has no material to mate, do drawn, Randompl - Steftcho, FICS, 2012) 9...Ke8 10.O-O (10.d3 c6 11.O-O d6 12.Bf4 Qf6 13.Ne2 Qe6 14.d5 cxd5 15.Nd4 Qf6 16.Qb5+ Kf7 17.Qxd5+ Kg6 18.e5 Qxf4 19.Ne6 Bxe6 20.Qxe6+ Kh5 21.Rae1 Black forfeited on time, papernoose - nuumm, FICS, 2004) 10...Be7 11.f4 Nf6 12.e5 Ng8 13.Ne4 d6 14.exd6 Bxd6 15.Re1 Kf8 16.Ng5 Qf6 17.Ne6+ Bxe6 18.Rxe6 Qxd4+ 19.Kh1 Bc5 20.Re3 b6 21.d3 Nf6 22.Bd2 Ng4 23.Re4 Nf2+ White resigned, bestcoast - Banjar, FICS, 2013; and
8.d5+ Ke7 9.d4 d6 10.Bg5+ Nf6 11.e5 h6 12.exf6+ gxf6 13.Bh4 Bg7 14.Qe2+ Kf8 15.O-O Bf5 16.Nc3 a6 17.Qf3 Bg6 18.Ne4 Kf7 19.Rae1 Re8 20.Ng3 Qd7 21.Rxe8 Rxe8 22.Ne2 Be4 23.Qh5+ Bg6 24.Qf3 Be4 25.Qh5+ Bg6 26.Qf3 Be4 27.Qb3 Bxg2 28.Re1 Bf3 29.Qxf3 Kg8 30.Kh1 f5 31.Rg1 Re4 32.Nf4 Qf7 33.Ne6 Rg4 34.Rxg4 fxg4 35.Qxg4 Kh7 36.f3 Bxd4 37.Qe4+ Kg8 38.Qxd4 Qxf3+ 39.Kg1 Black resigned, marciprevi - nchak, FICS, 2016
8...d6 9.f4
9...Ke7
9...Kf7 was seen in topsoul - moisesserraramos, lichess.org, 2016
10.f5 h6 11.e5
Understandable, but a bit premature, although it is tempting to hurry things up in a blitz game. Better was 11.Nc3.
11...dxe5 12.dxe5 Qd5
If Black wants to win the e-pawn he probably should start out with 12...Qd4+ 13.Kh1 Kd8 when there will be no danger of the Queen being pinned to her King.
13.Nc3 Qd4+ 14.Kh1 Ke8
Missing the advice of the previous note.
15.Qe2 Bd7
White has two pawns for his sacrificed piece, and a much safer King. He is better.
16.b3 a6 17.Bb2 Kd8 18.Rab1
It is clear that White want's to unmask his fianchettoed Bishop, but 18.Nd1!? might have been a better way to to that. Or he could patiently play 18.Rc1 instead.
18...Qh4 19.d4 Kc8 20.d5 b6 21.a4 Bc5 22.e6 Be8 23.Ne4
White has clearly taken control of the game.
23...Nf6 24.Nxf6
White prefers to hold onto his powerful Bishop, but he could have considered exchanging it, as after 24.Bxf6!? gxf6 25.g3!? Black's Queen will be nudged away from protecting the pawn at f6, e.g. 25...Qh5 26.Qc4 and the pawn will fall.
24...gxf6 25.Qf3 Bh5
Suddenly Black seems to be in charge.
26.Qd3
White had the alternative 26.Bxf6!? Bxf3 27.Bxh4 Bxd5 28.b4 Bd6 29.Rbd1 c6, but his "Jerome pawns" appear stalled.
26...Bd6 27.g3 Qg4
The clock seems to be affecting moves at this point.
28.Bxf6 Qe2
Missing the fact that after the exchange of Queens and then the "exhange" of Rooks, he would drop a piece, i.e. 29.Qxe2 Bxe2 30.Bxh8 Bxf1 31.Rxf1.
29.Qc3
Yikes! Tick, tick, tick... Black now has 29...Qe4+ 30.Kg1 Bc5+ winning White's Queen.
29...Bf3+
Seeing ghosts.
Now Black drops a piece, and the "Jerome pawns" advance menacingly.
30.Rxf3 Rg8 31. Bh4 Qe4 32. Rbf1 Qxd5 33. e7 Re8 34. f6 Bxe7 35.fxe7 Kb7
Cruel, cruel clock.
36.Kg1 Qc5+ 37.Qxc5 bxc5 38.Rf8 Kb6 39.Rxe8 Rxe8 40.Rf8 Rxe7 41.Bxe7
Here Black forfeited on time.
Recently I received a request for The Database from Rodolfo Pardi (librarian, Italian Chess Federation chess instructor and tournament director), the author of a good number of chess books, including A dreadful Chess Trap: Blackburne Shilling. He said he had been frequently meeting the Blackburne Shilling Jerome Gambit (1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Nd4 4.Bxf7+), and wanted to know more about it.Of course, I sent the (compressed) PGN file right away!In a recent email he said he had updated his book about the Blackburne Shilling Gambit, adding a section for the Blackburne Shilling Jerome Gambit and noting
As my book is aimed to the player with Black, I put a link to the following file, containing 600 games from your database [The Database] where Black plays Ke6 and ends winning. http://scacchi.vecchilibri.eu/partite/jeromeke6.htmlWow.
Rodolfo was referring to the line 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Nd4 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Ke6 and I thought I would take a closer look at it. The following game holds a lot of analysis and ideas - and also shows the practical side of the Blackburne Shilling Gambit, as complications bring the clock into play.
hanslenz - raidrunner
blitz, FICS, 2012
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Nd4 4.Bxf7+
The Blackburne Shilling Jerome Gambit. The Database has 5,337 game examples. White scores 56%. (Only 2% of the games are draws.)
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Ke6
Black's most enterprising response. Here The Database has 1,434 games, with White scoring 53%.
6.c3 Kxe5 7.cxd4+ Ke6
Wise. Black avoids a whole lot of trouble by declining the d-pawn and the e-pawn. Trust me. Or check out the wild analysis, below.
After 7...Kxd4?! 8.Qb3 we enter a line that shows up in exactly 0 games in The Database, and which has complications galore.
Stockfish 8 recommends 8...d5 (instead, grabbing the second pawn makes matters dangeously worse for Black: 8...Kxe4?! 9.d4! Bb4+!? 10.Nc3+!? Bxc3+ 11.bxc3 Qe7 12.g4!? Qe6 [12...Kf3+ 13.Be3 Kxg4 14.Rg1+ and mates] 13.c4 Qxg4 [13...Kxd4+ 14.Be3+ and mates] 14.Qc2+ Kxd4 15.Qb2+ Kd3 [15...Ke4 16.f3+!? Qxf3 17.Rf1 Qxf1+ 18.Kxf1 and wins] 16.Be3 Ke4 17.h3 Qg6 18.0–0–0 Qf6 19.Bd4 Qf4+ 20.Kb1 Kf5 21.Bxg7 d6 22.Bxh8 Ke6 23.Rhg1 and White is winning) 9.Nc3 Ne7 10.Nb5+!? (Or 10.exd5 Ke5 11.0–0 Kf6 12.d6 Kg6 [12...Nc6 13.Ne4+ Kg6 14.Qg3+ Kf7 15.Ng5+ Kf6 16.b4 Bxd6 17.Bb2+ Be5 18.Bxe5+ Nxe5 19.Ne4+ Kf7 20.Qf4+ Kg6 21.Qxe5] 13.dxe7 Bxe7 14.Re1 Re8 15.d4 Bd6 16.Bd2 h6 17.Nd5 c6 18.Nf4+ Bxf4 19.Bxf4 Rxe1+ 20.Rxe1 Qd5 21.Qxd5 cxd5 22.Re7 Kf6 23.Rc7 g5 1.52/27 ) 10...Ke5 11.Nxc7!? Rb8 (11...Qxc7? 12.Qg3+ Kf6 13.Qxc7) 12.d4+ Kf6 [only move] 13.Bf4 dxe4 14.0–0 h6 15.Rae1 b5 16.Be5+ Kg6 17.Ne6 Bxe6 18.Qxe6+ Kh7 19.Bxb8 Qxb8 20.Rxe4 Qc8 21.g3 Qxe6 22.Rxe6 Nf5 with the advantage to White of R+2P vs N+B.
If Black tries 7...Kxe4?! instead, White has 8.Qf3!? Kxd4 9.Nc3 (there are no games with this move in The Database) and Black will lose material trying to undo the mating web. For example, 9...c6 10.Qe3+ Kc4 11.a4!? Qe7 - trying to keep the White Queen out of the action by pinning it to the King - 12.b3!? and Black will lose his Queen after 12...Kb4 13.Ba3+ or be checkmated after 12...Kxb3 13.Ne4+ Kc4 14.Ba3!? Also a reasonable defensive try is 9...Qe7+, but after the logical 10.Kd1 White's King is far less uncomfortable, for example 10...Nf6 11.Qf4+ Kc5 12.Qxc7+ Kd4 13.Re1, winning the Queen. (See also "Regicide".)
8.O-O
Keeping his options open.
Also seen:
8.Nc3 Kf7 (8...Bb4, instead, is "A casual move that brings much misfortune"; see Clydeco - chaparov, standard, FICS, 2012) 9.Qb3+ (9.Qh5+ g6 10.Qf3+ Qf6 11.Qd3 Bg7 12.e5 Qa6 13.Qf3+ Ke8 14.d3 Ne7 15.O-O Rf8 16.Qh3 h5 17.Qg3 d6 18.Bg5 dxe5 19.Bxe7 Kxe7 20.Nd5+ Kd8 21.dxe5 Bf5 22.e6 Qd6 23.e7+ Ke8 24.exf8=Q+ Bxf8 25.Nxc7+ Kd7 26.Nxa8 Qxg3 27.fxg3 Bc5+ 28.d4 Bxd4+ 29.Kh1 Bxb2 30.Rab1 Bxb1 31.Rxb1 Ba3 32.Rxb7+ Kc6 33.Rxa7 Bc5 34.Rg7 Kb5 35.Rxg6 h4 36.gxh4 Kc4 37.Rg5 Be3 38.Rg3 Bf4 39.Rg4 Kd5 40.Rxf4 Kc6 41.h5 Kd6 42.h6 Ke6 43.h7 Ke5 44.Rf7 Ke6 45.h8=Q Kxf7 46.g4 Ke6 47.g5 Kf7 White ran out of time, Black has no material to mate, do drawn, Randompl - Steftcho, FICS, 2012) 9...Ke8 10.O-O (10.d3 c6 11.O-O d6 12.Bf4 Qf6 13.Ne2 Qe6 14.d5 cxd5 15.Nd4 Qf6 16.Qb5+ Kf7 17.Qxd5+ Kg6 18.e5 Qxf4 19.Ne6 Bxe6 20.Qxe6+ Kh5 21.Rae1 Black forfeited on time, papernoose - nuumm, FICS, 2004) 10...Be7 11.f4 Nf6 12.e5 Ng8 13.Ne4 d6 14.exd6 Bxd6 15.Re1 Kf8 16.Ng5 Qf6 17.Ne6+ Bxe6 18.Rxe6 Qxd4+ 19.Kh1 Bc5 20.Re3 b6 21.d3 Nf6 22.Bd2 Ng4 23.Re4 Nf2+ White resigned, bestcoast - Banjar, FICS, 2013; and
8.d5+ Ke7 9.d4 d6 10.Bg5+ Nf6 11.e5 h6 12.exf6+ gxf6 13.Bh4 Bg7 14.Qe2+ Kf8 15.O-O Bf5 16.Nc3 a6 17.Qf3 Bg6 18.Ne4 Kf7 19.Rae1 Re8 20.Ng3 Qd7 21.Rxe8 Rxe8 22.Ne2 Be4 23.Qh5+ Bg6 24.Qf3 Be4 25.Qh5+ Bg6 26.Qf3 Be4 27.Qb3 Bxg2 28.Re1 Bf3 29.Qxf3 Kg8 30.Kh1 f5 31.Rg1 Re4 32.Nf4 Qf7 33.Ne6 Rg4 34.Rxg4 fxg4 35.Qxg4 Kh7 36.f3 Bxd4 37.Qe4+ Kg8 38.Qxd4 Qxf3+ 39.Kg1 Black resigned, marciprevi - nchak, FICS, 2016
8...d6 9.f4
9...Ke7
9...Kf7 was seen in topsoul - moisesserraramos, lichess.org, 2016
10.f5 h6 11.e5
Understandable, but a bit premature, although it is tempting to hurry things up in a blitz game. Better was 11.Nc3.
11...dxe5 12.dxe5 Qd5
If Black wants to win the e-pawn he probably should start out with 12...Qd4+ 13.Kh1 Kd8 when there will be no danger of the Queen being pinned to her King.
13.Nc3 Qd4+ 14.Kh1 Ke8
Missing the advice of the previous note.
15.Qe2 Bd7
White has two pawns for his sacrificed piece, and a much safer King. He is better.
16.b3 a6 17.Bb2 Kd8 18.Rab1
It is clear that White want's to unmask his fianchettoed Bishop, but 18.Nd1!? might have been a better way to to that. Or he could patiently play 18.Rc1 instead.
18...Qh4 19.d4 Kc8 20.d5 b6 21.a4 Bc5 22.e6 Be8 23.Ne4
White has clearly taken control of the game.
23...Nf6 24.Nxf6
White prefers to hold onto his powerful Bishop, but he could have considered exchanging it, as after 24.Bxf6!? gxf6 25.g3!? Black's Queen will be nudged away from protecting the pawn at f6, e.g. 25...Qh5 26.Qc4 and the pawn will fall.
24...gxf6 25.Qf3 Bh5
Suddenly Black seems to be in charge.
26.Qd3
White had the alternative 26.Bxf6!? Bxf3 27.Bxh4 Bxd5 28.b4 Bd6 29.Rbd1 c6, but his "Jerome pawns" appear stalled.
26...Bd6 27.g3 Qg4
The clock seems to be affecting moves at this point.
28.Bxf6 Qe2
Missing the fact that after the exchange of Queens and then the "exhange" of Rooks, he would drop a piece, i.e. 29.Qxe2 Bxe2 30.Bxh8 Bxf1 31.Rxf1.
29.Qc3
Yikes! Tick, tick, tick... Black now has 29...Qe4+ 30.Kg1 Bc5+ winning White's Queen.
29...Bf3+
Seeing ghosts.
Now Black drops a piece, and the "Jerome pawns" advance menacingly.
30.Rxf3 Rg8 31. Bh4 Qe4 32. Rbf1 Qxd5 33. e7 Re8 34. f6 Bxe7 35.fxe7 Kb7
Cruel, cruel clock.
36.Kg1 Qc5+ 37.Qxc5 bxc5 38.Rf8 Kb6 39.Rxe8 Rxe8 40.Rf8 Rxe7 41.Bxe7
Here Black forfeited on time.
Labels:
Banjar,
bestcoast,
Blackburne Shilling Gambit,
chaparov,
Clydeco,
FICS,
hanslenz,
lichess.org,
marciprevi,
moisesserraramos,
nchak,
nuum,
papernoose,
Pardi,
raidrunner,
Randompl,
Steftcho,
topsoul
Wednesday, January 3, 2018
Jerome Gambit: Two English Amateurs
The following game ("between two English amateurs") is from the "OVER THE CHESS BOARD" column titled "A VARIATION OF THE JEROME GAMBIT", conducted by R. M. Baird, in the Evening Star of May 11, 1901.
It is amusing that the columnist cannot recommend the opening, grows impatient when White misses a forcing line - and has nothing to say when White wins.
I have added diagrams, changed the notation from descriptive to algebraic, and provided a few notes in blue. - Rick
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.d4 exd4 5.Bxf7+
It is interesting to meet with these variations from the ordinary dull methods. But this line of play cannot be recommended.
5...Kxf7
[Reaching the Jerome Gambit variation: 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7 5.d4 exd5]
6.Ng5+ Ke8 7.Qf3 Qe7
If now 7...Qf6 all of White's attack (?) vanishes. Black might even play 7...Ne5 at once.
8.O-O Ne5 9.Qb3 h6 10.Nh7
[Strange. Perhaps expecting 10...Rxh7? 11.Qxg8+ Qf8 12.Qxh7, winning. Black does not fall for the "trap".]
10...g6 11.f4 d3+ 12.Kh1 Ng4 13.f5 Qxh7
14.fxg6 Qxg6 15.Nc3 Qh5 16.Bf4 Nf2+
17.Rxf2 Bxf2 18.Rf1 Bd4 19.Nd5 Bb6
20.Bxc7 d6
[Amazing. Ahead by a Bishop and a Rook, Black finds a move that gives himself a lost game.]
21.Bxd6 Qg6
22.Rf8+
Much easier and simpler was 22.Qb5+ and mate in two moves.
22...Kd7 23.e5 Ne7 24.Qb5+ Nc6 25.Nf6+ Ke6 26.Qd5+ Kf5 27.e6+ Black resigned
It is amusing that the columnist cannot recommend the opening, grows impatient when White misses a forcing line - and has nothing to say when White wins.
I have added diagrams, changed the notation from descriptive to algebraic, and provided a few notes in blue. - Rick
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.d4 exd4 5.Bxf7+
It is interesting to meet with these variations from the ordinary dull methods. But this line of play cannot be recommended.
5...Kxf7
[Reaching the Jerome Gambit variation: 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7 5.d4 exd5]
6.Ng5+ Ke8 7.Qf3 Qe7
If now 7...Qf6 all of White's attack (?) vanishes. Black might even play 7...Ne5 at once.
8.O-O Ne5 9.Qb3 h6 10.Nh7
[Strange. Perhaps expecting 10...Rxh7? 11.Qxg8+ Qf8 12.Qxh7, winning. Black does not fall for the "trap".]
10...g6 11.f4 d3+ 12.Kh1 Ng4 13.f5 Qxh7
14.fxg6 Qxg6 15.Nc3 Qh5 16.Bf4 Nf2+
17.Rxf2 Bxf2 18.Rf1 Bd4 19.Nd5 Bb6
20.Bxc7 d6
[Amazing. Ahead by a Bishop and a Rook, Black finds a move that gives himself a lost game.]
21.Bxd6 Qg6
22.Rf8+
Much easier and simpler was 22.Qb5+ and mate in two moves.
22...Kd7 23.e5 Ne7 24.Qb5+ Nc6 25.Nf6+ Ke6 26.Qd5+ Kf5 27.e6+ Black resigned
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)