Even in the non-main-line lines of the non-main-line Jerome Gambit, there is theory, and practice, as Philidor1792 demonstrates in the game below.
Philidor1792 - jenskun
Russia Central Federal District vs Phil,
Chess.com, 2015
1.e4 e5 2. Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7
5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.Qh5+ Ng6 7.Qd5+ Ke7
Infrequently played, but not bad.
8. Qxc5+
The experimental 8.Qg5+ was tried in Wall,B - CKFM, FICS, 2012 (1-0, 44).
8... d6 9. Qe3
The Database has three games with 9.Qg5+: fehim - Schiele, FICS, 2006, (0-1, 59); stampyshortlegs - calchess10, JGTourney4, ChessWorld 2009 (1-0, 31); and Wall,B - Vassilev,R, Chess.com, 2010 (1-0, 32).
9... Be6
Instead, 9... Nf6 was seen in three MrJoker games: MrJoker - Yuvi, ICC, 2011 (1-0, 16); MrJoker - Cleanbishop, ICC, 2012 (1-0, 46); and MrJoker - taz, ICC, 2013 (1-0, 43).
The Bishop move seems to invite f2-f4 by White, gaining a tempo.
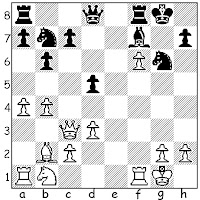
10.O-O Nf6 11.f4 Bf7 12.f5 Ne5 13.d4 Nc6 14.e5 dxe5 15.dxe5 Nd5 16.Qg3 Kf8
The extra tempo for White, the "Jerome pawns" and Black's uneasy King have lead to an equal game. As we have frequently seen in Jerome Gambit lore, when White has equalized, he has the advantage.
17.Bg5 Qc8 18.e6 Bh5 19.Nc3 Nxc3 20.Qxc3 Rg8 21.f6 gxf6 22.Qxf6+ Ke8 23.Rad1 Qd8 24.Rxd8+ Rxd8 25.b4 b5 26.a4 a6 27.axb5 Black resigned
The question arises, again: how much work do you have to do to beat Bill Wall's Jerome Gambit?
Wall,B - JKBK
FICS, 2012
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.Qh5+ Ng6 7.Qd5+ Ke7 8.Qxc5+
There is also the interesting 8.Qg5+, seen in Wall,B - CKFM, FICS, 2012 (1-0, 44).
8...d6 9.Qa5
Or, for variety, there still is 9.Qg5+ as in billwall - buhov, Chess.com, 2010 (1-0, 32).
9...Nf6 10.0-0 b6 11.Qa3 Rf8
This certainly seems correct: while White runs his Queen around, Black castles-by-hand and safeguards his monarch.
12.f4 Kf7 13.f5 Ne7 14.Qb3+ d5 15.e5 Ne4 16.d3 Nc5 17.Qc3 Kg8
18.b4 Nb7 19.f6 Ng6 20.a4 gxf6 21.exf6 Be6 22.Bb2 Bf7
23.Qd2 Nd6?
How fragile the position... This allows White to equalize, which is almost like a winning advantage for Mr. Wall.
24.Qh6 Ne8 25.Nd2 d4
How can shutting out the White Bishop be wrong? When it lets the White Knight in.
26.Ne4 Bd5 27.Ng5 Qd7 28.f7+
Remember me?
28...Rxf7 29.Rxf7 Bxf7 30.Qxh7+ Kf8 31.Rf1 Nd6 32.Qxg6 Black resigned
Black will lose significant material.
The latest, from Bill Wall.
Wall,B - Guest497592
Playchess.com, 2012
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.Qh5+ Ng6
7.Qd5+ Ke8
The interesting 7...Ke7 8.Qg5+ appeared in Wall,B - CKFM, FICS, 2012 (1-0, 44).
8.Qxc5 Qe7 9.Qe3 d5
Or 9...Nf6 10.Nc3 d6 11.0-0 Be6 (11...Ng4 12.Qg3 Qe5 13.Nd5 Qxg3 14.fxg3 Kd7 15.Rf7+ Wall,B - CKSP, FICS, 2010 (1-0, 15)) 12.f4 Ng4 13.Qg3 Qh4 14.Qxh4 Nxh4 15.g3 Nf5 16.exf5 Bxf5 17.Re1+ Kd7 18.d3 Rae8 19.Bd2 c6 20.h3 Wall,B -Hirami,Z, Chess.com, 2011 (1-0, 20).
10.Nc3 dxe4 11.Nxe4 Nf6 12.d3 Ne5 13.0-0 Nfg4
"When at a loss for a move, you can always threaten White's Queen." NOT.
14.Qe2 Bf5 15.Bg5 Qd7?
Better 15...Nf6.
16.h3 h6 17.Nc5 Qc6 18.hxg4 hxg5
This grants White a large advantage.
19.Qxe5+ Be6 20.Nxe6 Kd7
Mate follows. "Best" is the miserable 20...Qd6 21.Nxc7+
21.Qxg7+ Kxe6 22.Rfe1+ Kd5 23.Qe5 checkmate
From Wikipedia: "MacGyver is an American action-adventure television series... [S]ecret agent Angus MacGyver... is a resourceful agent with an encyclopedic knowledge of science, able to solve complex problems with everyday materials he finds at hand, along with his ever-present duct tape and Swiss Army knife."
Playing over the following game, I got to thinking about MacGyver.
Bill Wall's opponent had navigated the game into a tricky, but draw-able, Bishops-of-opposite-colors endgame, where it seemed possible that Black might actually extract a half-point from White's Jerome Gambit (a rare event, to be sure).
What did Bill have to work with at the end?
Ah, but it is the "+" on White's last move that gives the win.
Wall,B - CKFM
FICS, 2012
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+
4...Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5 6.Qh5+ Ng6
7.Qd5+ Ke7 8.Qg5+
Something new! There are no other examples in The Database.
Black has a chance to slip, but the game transposes to more "normal" lines.
8... Ke8 9.Qxc5 Qe7 10.Qe3 Nf6 11.Nc3 Kf7
Or 10...d6 11.0-0 Ng4 (11...Be6 12.f4 Ng4 13.Qg3 Qh4 14.Qxh4 Nxh4 15.g3 Nf5 16.exf5 Bxf5 17.Re1+ Kd7 18.d3 Rae8 19.Bd2 c6 20.h3 Black resigned, Wall,B - Hirami,Z, Chess.com, 2011) 12.Qg3 Qe5 13.Nd5 Qxg3 14.fxg3 Kd7 15.Rf7+ Black resigned, Wall,B -CKSP, FICS, 2010.
12.0-0 Re8 13.d3 d5
Giving a pawn back to be able to exchange Queens.
14.Nxd5 Nxd5 15.exd5 Qxe3 16.fxe3+ Kg8
White has three pawns for his sacrificed piece. Perhaps a super-GM like Magnus Carlsen would say that the game here is won for Black, and all that is left is a matter of (his) technique.
In the world of club players, however, it is not naive to see the game as balanced. The winner will be the one who handles his pawns/Knight better.
17.e4 Bg4 18.Be3 a6 19.Rf2 Rad8 20.h3 Bd7 21.Raf1 c6 22.Bb6 Rc8 23.d6
One "Jerome pawn" gets through. The game is still about even, but that's one more thing for Black to worry about, and one more thing for White to rely on.
23...Be6 24.d4 Nf8 25.g4 Bc4 26.Rxf8+
Possibly this Rook sacrifice was a surprise for Black.
26...Rxf8 27.Rxf8+ Rxf8 28.d7 Bxa2
Of course, White will get his Rook back when he promotes the d-pawn, so Black grabs some "compensation."
29.e5 Kf7 30.d8Q Rxd8 31.Bxd8 Ke6
The excellent placement of Black's King makes the Bishops-of-opposite-colors endgame even, even though White has an extra pawn.
32.Kf2 Bb1 33.c3 Ba2 34.Kf3 Kd5 35.Kf4 Ke6 36.Kg5 Kf7 37.h4 Bb1
White looks to see what he can create on the Kingside. If he is able to advance his center two pawns, that will allow Black some counterplay with his remaining 2:1 pawn majority on the Queenside. Eventually White will have to exchange one of his center pawns for a Black wing pawn, and the other White center pawn will be safely blockaded.
38.h5 h6+ 39.Kh4 g6 40.hxg6+ Kxg6 41.e6 Ba2 42.e7 Bf7 43.c4
Things are looking a bit scary for Black right now. Suppose he loses a tempo with 43...Be8. White quickly advances in the center with 44.d5 cxd5 45.cxd5 and has those scary two passers.
But, what would happen next? After 45...Kf7 White can liquidate the Kingside with 46.g5 hxg5+ 47.Kxg5 but now Black starts rolling on the Queenside with 47...a5. Since swapping his Pe7 for the ambitious, but lowly, Pa5 is seriously draw-ish, White's King must persevere with 48.Kf5.
After 48...a4 49.Ke5 b5 50.d6 (50.Kd6 will face the same response) b4 51.Bb6 a3 52.b3 Bc6 53.Bc5 a2 54.Bd4 Bf3
analysis diagram
Black's and White's advanced passers hold each other hostage and the point can be split, especially after 55.Bb2 Bd1 56.Kc5 Bxb3+.
That kind of pressure, though, searching for that kind of solution, can cause the defender to slip.
43...Kf6 44.e8Q+ Black resigned
The discovered check allows the pawn to Queen safely, and now White can force checkmate.
(Along with his Swiss army knife and duct tape, you had to figure that MacGyver had a discovered check on him, somewhere.)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)