[Continued from Christmas.]
So far, the close look at my recent Jerome Gambit game has progressed a half-dozen moves. See "Merry Christmas! A Hysterical/Historical Jerome Gambit, Part 1".
Again, I have historical information from my never-published article submitted to Stefan Bucker for his magazine Kaissiber (and revised, and revised, and revised, and revised, and reassessed).
blitz, FICS, 2013
perrypawnpusher - spince
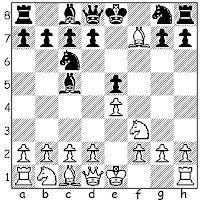
1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Kf8 6.Nxc6 dxc6
This position was reached in his first article with analysis of the Jerome Gambit (Dubuque Chess Journal 4/1874) by Alonzo Wheeler Jerome.
As early as July 1874 it was clear that Alonzo Wheeler
Jerome had no illusions about his gambit, as the Dubuque Chess Journal noted
It should be
understood that Mr. Jerome claims in this New Opening "only a pleasant
variation of the Giuoco Piano, which may win or lose according to the skill
of the players, but which is capable of affording many new positions and
opportunities for heavy blows unexpectedly.
This modesty did not prevent Jerome from debating for months with William Hallock, who produced the American Chess Journal in
the years following the demise of the Dubuque Chess Journal. While
testing his invention in over-the-board and correspondence play, Jerome claimed
…that
the opening has a “reasonable chance of winning,” which
is sufficient to constitute a “sound opening.” It is not required that
an Opening shall be sure to win. There is no such opening contained
in chess; at least none that I know of.
In
the exchanges of games and analysis that appeared in the American Chess Journal in 1876 and
1877, Hallock progressed from referring to “Jerome’s Double Opening” to
“Jerome’s Gambit” to “Jerome’s Absurdity.”
This
light-hearted approach found full form in the May 1877 issue of the Danish
chess magazine Nordisk Skaktidende, where Lieutenant Sorensen, analyzed the Jerome Gambit in
his “Chess Theory for Beginners” column:
With this
answering move of the Bishop [1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5] we have the
fundamental position for that good old game which the Italians, hundreds of
years ago, when they were masters of the Chessboard, called "Giuoco
Piano," even game, but the later age, for generality of explanation, the
"Italian game." On this basis the usual continuation is 4.c3, whereby
the QP at the next move threatens to advance, and the White middle
Pawns to occupy the centre. In the next articles we will make mention
of that regular fight for the maintenance or destruction of the
center, which is the essential point of the Italian game; in this, on
the contrary, we will occupy ourselves with a Bashi-Bazouk attack, over
which the learned Italians would have crossed themselves had they
known it came under the idea of piano, but which is in
reality of very recent date - 1874, and takes it origin from an American, A.W.
Jerome. It consists in the sacrifice of a piece by 4.Bxf7+. Naturally we
immediately remark that it is unsound, and that Black must obtain the
advantage; but the attack is pretty sharp, and Black must take exact care, if
he does not wish to go quickly to the dogs. A little analysis of it will,
therefore, be highly instructive, not to say necessary, for less practiced
players, and will be in its right place in our Theory, especially since it
is not found in any handbook. The Americans call the game
"Jerome's double opening," an allusion, probably, to the fresh sacrifice of
a piece which follows at the next move, but we shall prefer to use
the short and sufficiently clear designation, Jerome Gambit.
The August 1877 issue of the British Chess Player’s Chronicle and the December 1877 issue of the Italian Nuova Rivista Degli Scacci, reprinted Sorensen’s article (in English and Italian, respectively),
introducing the Jerome Gambit to an even wider audience. Almost every Jerome Gambit analyst since has leaned heavily on Sorensen.
Interest in the Jerome Gambit did not remain just among beginning chess players. A couple of years later, Andres Clemente Vazquez included three wins with the Gambit, from his 1876 match against Carrington, in his Algunas Partidas de Ajedrez Jugadas in Mexico por Andres Clemente Vazquez.
G. H. D. Gossip’s 1879 book, Theory of the Chess Openings, included an analysis of the Jerome Gambit, “substantially the same” as that which appeared in the Chess Player’s
Chronicle, as the latter noted in a review of the work. At about the same
time, the American daily newspaper, the Cincinnati Commercial Gazette,
in its chess column, struck the right tone in its review of Theory,
noting gleefully
...the Jerome
Gambit, which high-toned players sometimes affect to despise because it is radically
unsound, finds a place, and to this it is certainly entitled.
The next year, in 1880, when the 6th
edition of the illustrious Handbuch des Schachspiels was published, the Commercial
Gazette’s chess columnist was again ready to “complain” about the
state of affairs
…that the
"Jerome Gambit" should be utterly (even if
deservedly) ignored.
The Cincinnati
connection is an important one in the story of the development of the Jerome
Gambit. In the 1870 and 1880s, the chess column of the Commercial Gazette,
conducted by J. W. Miller, was considered to be one of the best in the United
States. It occasionally ran opening analysis
presented by S. A. Charles, a member of the local chess club. By January 1881,
Charles had switched to sending his analyses to the Pittsburgh Telegraph (later,
the Chronicle-Telegraph).
In October 1881, the Jerome Gambit
broke onto the international scene again, in Brentano's Chess Monthly,
(edited by H.C. Allen & J.N. Babson), with a letter and analysis from S. A.
Charles.
The November 2, 1881 chess column in the Pittsburgh
Telegraph ran Charles’ corrected and slightly updated version of his
analysis from Brentano's Chess Monthly.
The year 1882 brought yet more attention, from
respectable sources, to the Jerome Gambit. William Cook, with the assistance of
E. Freeborough and C. E. Ranken, brought out the third edition of his Modern
Chess Openings-style Cook's Synopsis of the Chess Openings A Tabulated
Analysis.
7.0-0
Like in the "annoying defense" against the Jerome Gambit (1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Bc5 4.Bxf7+ Kxf7 5.Nxe5+ Nxe5+ 6.Qh5+ Ke6 7.f4 d6 8.fxe5 dxe5, etc.), Black has returned a piece to achieve a static position that limits White's attacking chances.
Here, though, White has the long-term plan of developing and deliberately advancing his "Jerome pawns". If Black is watchful during this process, he can probably return a second piece for two pawns and sue for peace.
Also played (often transposing) has been 7.d3, as in perrypawnpusher - Jore, blitz, FICS, 2011 (0-1, 16); perrypawnpusher - Conspicuous, blitz, FICS, 2011 (1-0, 13); perrypawnpusher - fortytwooz, blitz, FICS, 2010 (1-0, 29); perrypawnpusher - Lark, blitz, FICS, 2011 (1-0, 12); perrypawnpusher - pitrisko, blitz, FICS, 2011 (0-1, 30); and Wall,B - WMXW, FICS, 2012 (1-0, 31).
7.Nc3 (followed by 8.d3 and 9.0-0 ) was seen in perrypawnpusher - Ykcir, FICS, 14 0 blitz, 2009 (½-½, 11).
7.c3 was seen in Vazquez,A - Carrington,Wm, Mexico, 2nd match 1876 (1-0, 43).
7...Be6
7...Nf6 was popular in the early games of this line, as in Jerome,A - Brownson,O, Iowa 1875 (½-½, 29); Norton,D - Hallock,A, correspondence, 1877 (0-1,18), Lowe,E - Parker,J, correspondence, 1879, (0-1, 25); and Lowe,E - Parker,J, correspondence, 1879 (1-0, 37).
Subsequent analysis has generally followed Jerome - Brownson, Iowa, 1875, with 7.O-O Nf6 8.Qf3 (Sorensen said 8.e5 would be met by 8…Bg4 9.Qe1 Kf7! which was how Norton – Hallock had continued ) Qd4 9.d3 Bg4 10.Qg3. At this point, Brownson played 10…Bb6. Jerome responded with 11.e5, and drew the game, with help from his opponent, in 29 moves. Brownson, in the Dubuque Chess Journal (3/1875), suggested 11.Kh1 and 12.f4 as an improvement for White.
Sorensen, Nordisk Skaktidende, (5/1877) gave the alternative line 10…Bd6, attacking White’s Queen, and followed this up with 11.Bf4 g5 12.Bxd6+ cd 13.h3 Be6 14.Qxg5 Rg8 15.Qh6+ Ke7 16.Nc3 Rg6 17.Qh4 Rag8 with a better game for Black. However, Charles later in the Pittsburg Telegraph (4/27/81) offered 11.c3 as an improvement, suggested to him by Jerome, which they believed reversed the valuation of the line.
As an historical aside, later sources, relying on - read: copying - Sorensen’s analysis, miss 11.c3; those that follow - read: copy - Charles’ work, based on his Brentano article or on the American Supplement, include it.
8.d3
Better than my goofball 8.Qf3+ from perrypawnpusher - CorH, blitz, FICS, 2009 (0-1, 74).
8...Qf6 9.Nc3 Ne7 10.Be3 Bd6
[To Be Continued on my birthday January 13, 2014.]
[Comments and Emails are Welcomed and Encouraged.]

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)